Introduction
Fiberglass rebar (GFRP) is rapidly gaining popularity as a corrosion-resistant alternative to traditional steel rebar. But working with GFRP presents unique challenges. Unlike steel, it’s brittle and requires precise techniques for cutting and bending.
In this article, we’ll explore how fiberglass rebar differs from steel, the tools and methods needed for cutting and bending, and the best practices for using it in construction. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of how to handle GFRP effectively.

Understanding Fiberglass Rebar and Its Uses
What is Fiberglass Rebar Made Of?
Fiberglass rebar consists of continuous glass fibers embedded in a polymer resin. This composite material is manufactured using a process known as pultrusion, where the fibers are pulled through a resin matrix to create a strong yet lightweight reinforcement material. The glass fibers provide tensile strength that is typically 2-3 times higher than steel, while the resin holds everything together, providing stability and durability.
However, GFRP is also more brittle in bending compared to steel. Its rigidity means it is not suited for on-site bending, and attempts to do so can lead to cracks or structural failure. This is why careful planning and the right tools are essential when cutting and handling fiberglass rebar. The material’s strength in tension makes it an ideal option for reinforcement in areas exposed to moisture and other harsh conditions, but its vulnerability to bending requires careful consideration during installation.
Common Applications of Fiberglass Rebar
Fiberglass rebar is primarily used in environments where steel reinforcement would corrode quickly, such as in coastal structures, bridges, and parking garages. It is especially beneficial in marine environments where the rebar is exposed to saltwater, which is highly corrosive to steel. Some of the most common applications include:
Bridge Construction: Used in decks and piers to resist corrosion from de-icing salts and water. GFRP rebar is an excellent choice for bridges located in areas with high humidity or exposure to saltwater.
Marine Structures: Ideal for piers, docks, and seawalls exposed to saltwater. The non-corrosive nature of fiberglass rebar ensures that these structures remain intact, even in the harshest maritime environments.
Chemical Processing Plants: Used in areas with aggressive chemicals that would corrode steel. GFRP rebar offers long-lasting reinforcement in environments where traditional steel rebar would fail due to chemical exposure.
Parking Garages: Protects against the corrosion caused by de-icing salts used on roads. The resistance to saltwater corrosion makes fiberglass rebar a reliable option for parking structures, especially in cold climates.
Essential Tools for Cutting Fiberglass Rebar
Manual and Power Tools for Cutting Rebar
To cut fiberglass rebar effectively, it's crucial to use the right tools. Here's a breakdown of tools suited for different cutting tasks:
Manual Tools:
Carbide-tipped hacksaw: Best for making smaller cuts with high precision. This tool is ideal for light-duty projects or when working with smaller pieces of rebar.
Utility knife: Suitable for trimming resin coatings after the rebar is cut. It is a handy tool when working with thinner rebar or when fine adjustments are needed.
Power Tools:
Angle grinder with diamond blade: The most efficient tool for cutting through larger pieces of fiberglass rebar. The diamond blade ensures clean cuts while minimizing fiber splintering, which is crucial for maintaining the material's integrity.
Circular saw with carbide blade: Ideal for bulk cutting at consistent lengths. This tool provides greater speed and accuracy, making it perfect for projects that require cutting multiple pieces to the same size.
| Tool Type | Example Tools | Best For | Advantages |
| Manual Tools | Carbide-tipped hacksaw, Utility knife | Small, precise cuts | Lightweight, easy to control |
| Power Tools | Angle grinder with diamond blade, Circular saw | Bulk cutting, Larger projects | Faster, more efficient, clean cuts |
Choosing the Best Tool for Your Cutting Job
The choice of cutting tool depends largely on the project and the environment:
Fieldwork: For on-site cutting, tools like angle grinders or utility knives are portable and effective. These tools are perfect when you need quick and efficient cuts on construction sites.
Shop Work: For more precision, a diamond blade saw can provide smoother cuts with minimal splintering. In a controlled shop environment, a circular saw with carbide blades ensures a high-quality cut with fewer rough edges.
Heavy-Duty Projects: When cutting large quantities of rebar, using a circular saw with a carbide blade ensures efficiency and consistency. This method is ideal for larger construction projects requiring the processing of multiple pieces of rebar quickly.
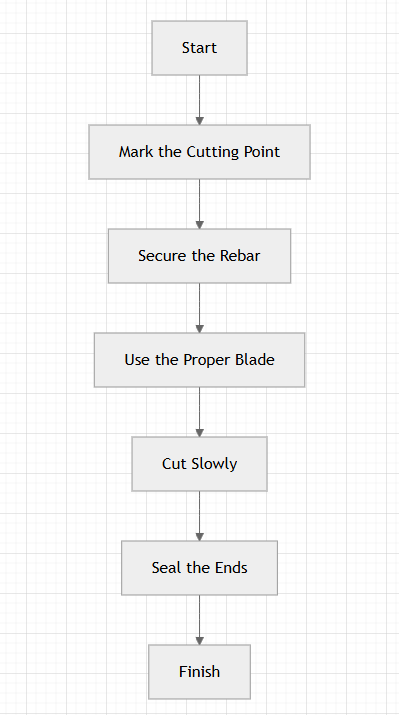
Step-by-Step Guide to Cutting Fiberglass Rebar
Follow these steps to cut fiberglass rebar safely and effectively:
Mark the Cutting Point: Use a permanent marker or masking tape to indicate where the rebar will be cut. Marking the cut line accurately ensures that you make clean and precise cuts.
Secure the Rebar: Ensure the rebar is firmly clamped to prevent vibration, which could cause uneven cuts or splintering. Use sturdy clamps to hold the rebar in place during the cutting process.
Use the Proper Blade: For best results, use a diamond or carbide-tipped blade. These blades are designed to handle the tough nature of fiberglass rebar and provide smooth, clean cuts.
Cut Slowly: To avoid overheating and damage to the resin, maintain a slow and steady cutting pace. Rushing through the cut can cause the resin to burn, which may weaken the rebar.
Seal the Ends (Optional): After cutting, apply epoxy or resin to the cut ends to prevent fiber exposure. Sealing the ends can also help protect the material from moisture and prevent any potential degradation over time.
Limitations of Bending Fiberglass Rebar
Why You Can't Bend Fiberglass Rebar on Site
Unlike steel rebar, fiberglass rebar cannot be bent on-site without risking damage. Fiberglass is much more brittle, and bending it beyond its designed limits can cause cracking or failure. Steel rebar, on the other hand, is ductile and can be bent on-site to fit various structural needs.
Fiberglass rebar’s brittleness makes it unsuitable for on-site bending. Attempting to bend it on-site can cause it to break or splinter, which compromises its structural properties. To maintain the strength and durability of the rebar, it should only be bent under controlled conditions at the factory.
Benefits of Factory Pre-Bent Fiberglass Rebar
Factory pre-bent fiberglass rebar is available in several shapes, such as U-shapes, L-shapes, and stirrups, providing significant advantages:
Accuracy: Pre-bent rebar ensures that the shapes are consistent and meet engineering specifications. This helps reduce the risk of errors during construction.
Reduced Labor Costs: Pre-bent rebar eliminates the need for on-site bending, saving time and labor costs. This is particularly useful in large-scale projects where efficiency is critical.
Enhanced Structural Integrity: Factory bending ensures that the rebar will not break or crack during the bending process, maintaining its strength and performance in the final structure.
Alternative Solutions for Bending Rebar on Site
While bending fiberglass rebar on-site is not recommended, there are alternative solutions:
Mechanical Connectors: These can be used to join straight sections of rebar together without the need for bending. Connectors provide a reliable way to reinforce structures without compromising the rebar.
Pre-Bent Sections: Instead of bending on-site, use pre-bent fiberglass rebar to create the necessary shapes. This ensures that the material maintains its integrity and strength.
Safety Measures When Cutting and Handling Fiberglass Rebar
Essential PPE for Cutting and Handling Rebar
Cutting and handling fiberglass rebar produce fine dust and sharp splinters, making personal protective equipment (PPE) essential. The following protective gear should always be worn:
| PPE Required | Purpose |
| Safety goggles | Protect eyes from debris and fiberglass dust |
| Respirator (N95 or higher) | Prevent inhalation of fiberglass particles |
| Cut-resistant gloves | Protect hands from splinters and sharp edges |
| Long sleeves and pants | Prevent skin irritation from fiberglass exposure |
Cutting Safety Tips to Prevent Injury
When cutting fiberglass rebar, always follow these safety tips:
Ventilation: Cut in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fiberglass dust. Proper ventilation helps reduce the risk of respiratory issues.
Avoid Skin Contact: Fiberglass splinters can cause skin irritation, so always wear protective clothing to prevent exposure. If you do get splinters, remove them carefully with tape.
Proper Tool Usage: Ensure the cutting tool is in good condition and use it according to manufacturer instructions. Proper maintenance of tools ensures a safer and more efficient cutting process.
Common Mistakes When Cutting and Bending Fiberglass Rebar
Mistakes to Avoid When Cutting Fiberglass Rebar
Using Incorrect Blades: Using wood or metal blades can cause splintering. Always opt for carbide-tipped or diamond blades that are designed for use with fiberglass materials.
Cutting Too Quickly: This can lead to uneven cuts, overheating, and damage to the rebar. Always cut slowly and apply steady pressure to maintain control over the cutting process.
Mistakes to Avoid When Bending Fiberglass Rebar
Attempting On-Site Bending: As mentioned earlier, fiberglass rebar should never be bent on-site. If bending is required, always use pre-bent sections or mechanical connectors to ensure structural integrity.
Over-Bending: If bending is required, use the appropriate methods and tools. Never exceed the bending limits of fiberglass rebar, as this can cause fractures.
How to Prevent Cutting and Bending Errors
Use Proper Tools: Always use the correct tools for the job to prevent mistakes. Ensure that your tools are well-maintained and suitable for cutting fiberglass rebar.
Measure Carefully: Ensure accurate measurements and markings before cutting or installing the rebar. Proper measurements help prevent errors that could affect the project’s outcome.
Follow Safety Protocols: Proper safety measures will help prevent accidents and ensure a clean and safe working environment.

Cost Considerations for Cutting and Pre-Bent Fiberglass Rebar
Cost of Cutting vs. Pre-Bent Fiberglass Rebar
Fiberglass rebar is typically priced between $0.70 and $1.10 per meter for straight pieces, with custom cutting and pre-bent rebar costing more:
Custom Pre-Cut Rebar: Can cost 10–15% more than standard rebar. This cost is justified by the time and labor savings during installation.
Pre-Bent Rebar: Factory-made pre-bent fiberglass rebar can cost 20–30% more but ensures better quality and durability. The higher upfront cost pays off in the long run due to reduced labor and fewer errors.
| Type of Fiberglass Rebar | Price per Meter | Additional Costs | Advantages/Disadvantages |
| Standard Fiberglass Rebar | $0.70 - $1.10 | None | Lower cost, suitable for most general projects |
| Custom Pre-Cut Fiberglass Rebar | 10-15% higher | Custom cutting and fabrication fees | Precise cuts, reduces labor costs on-site |
| Pre-Bent Fiberglass Rebar | 20-30% higher | Factory bending charges | Accurate shapes, reduces labor time and errors on-site |
How Pre-Cut and Pre-Bent Rebar Can Save You Money
While pre-bent rebar comes with a higher initial cost, it can save money in the long run by reducing labor costs and minimizing the risk of errors during construction. Additionally, pre-bent rebar is more accurate, which helps prevent structural issues that could lead to expensive repairs. In large-scale projects, using pre-bent rebar is a cost-effective choice that offers long-term value.
Conclusion
Cutting and bending fiberglass rebar requires the right tools and techniques to ensure safety and structural integrity. Always choose appropriate equipment, wear protective gear, and consider the benefits of pre-cut or pre-bent rebar for large-scale projects. Following these best practices ensures a cost-effective, secure installation.Anhui SenDe New Materials Technology Development Co., Ltd. offers advanced fiberglass rebar solutions that enhance durability and provide excellent corrosion resistance, adding significant value to construction projects.
FAQ
Q: What is Fiberglass Rebar and how is it different from steel rebar?
A: Fiberglass rebar is made from glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, offering excellent tensile strength. Unlike steel, it is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and more brittle, making it unsuitable for on-site bending.
Q: Can Fiberglass Rebar be bent on-site like steel rebar?
A: No, Fiberglass Rebar is too brittle to be bent on-site. It should be pre-bent in a factory or joined with mechanical connectors to avoid cracking.
Q: What tools are best for cutting Fiberglass Rebar?
A: To cut Fiberglass Rebar, use tools like carbide-tipped hacksaws or power tools such as angle grinders with diamond blades. These ensure clean and precise cuts.
Q: How does Fiberglass Rebar compare to traditional steel rebar?
A: While Fiberglass Rebar is more resistant to corrosion, it is also more brittle than steel and requires specific tools and techniques for cutting and installation.
Q: What are the advantages of using pre-bent Fiberglass Rebar?
A: Pre-bent Fiberglass Rebar offers precise shapes and reduces on-site labor costs, ensuring structural integrity and saving time compared to bending on-site.
Q: How do I ensure a safe process when cutting Fiberglass Rebar?
A: Always wear protective gear such as goggles, gloves, and a respirator. Use proper tools, cut slowly, and ensure good ventilation to avoid inhaling fiberglass dust.































